1. Introduction
Decentralized Finance (DeFi) refers to a new paradigm in the financial industry that leverages blockchain technology and smart contracts to provide open, permissionless, and decentralized financial services. This article provides a comprehensive overview of DeFi, including its definition, key features, how it works, key components, benefits, challenges, and the future outlook of this rapidly evolving sector.
2. What is Decentralized Finance (DeFi)?
Definition of DeFi
Decentralized Finance, or DeFi, is a system that aims to recreate traditional financial instruments and services in a decentralized and trustless manner. It eliminates the need for intermediaries, such as banks and financial institutions, by utilizing blockchain technology and smart contracts to enable peer-to-peer financial transactions.
Key Features of DeFi
- Decentralization: DeFi operates on decentralized networks, primarily blockchain platforms, where no single entity has control over the system.
- Openness: DeFi protocols are open-source, allowing anyone to inspect, verify, and contribute to their development.
- Interoperability: DeFi protocols can seamlessly interact with each other, creating a connected ecosystem of decentralized applications (DApps) and services.
- Permissionless: DeFi platforms are accessible to anyone with an internet connection, without the need for intermediaries or extensive documentation.
- Transparency: All transactions and operations within DeFi are recorded on the blockchain, providing a transparent and immutable audit trail.
3. How Does DeFi Work?
Blockchain Technology
DeFi relies on blockchain technology, which is a distributed ledger that records all transactions across a network of computers. This technology ensures transparency, immutability, and security of financial transactions.
Smart Contracts
Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. They automatically execute predefined actions when specific conditions are met, eliminating the need for intermediaries and ensuring trustless transactions.
Decentralized Applications (DApps)
DeFi applications, known as DApps, are built on blockchain platforms and operate in a decentralized manner. These applications interact with smart contracts and enable users to access various financial services, such as lending, borrowing, trading, and investing, directly from their wallets.
Tokenization
Tokenization is a key concept in DeFi, where real-world assets, such as currencies, securities, or commodities, are represented as digital tokens on the blockchain. These tokens can be easily traded, transferred, and stored, enabling fractional ownership and increased liquidity.
4. Key Components of DeFi
Decentralized Exchanges (DEXs)
DEXs are platforms that facilitate peer-to-peer cryptocurrency trading without the need for intermediaries. They operate using smart contracts, allowing users to trade directly from their wallets while maintaining control of their funds.
Decentralized Lending and Borrowing
DeFi platforms enable individuals to lend their digital assets and earn interest or borrow assets by providing collateral. These lending and borrowing protocols operate autonomously, matching lenders with borrowers through smart contracts.
Stablecoins
Stablecoins are cryptocurrencies designed to maintain a stable value by pegging them to an underlying asset, typically a fiat currency like the U.S. Dollar. Stablecoins provide stability within the volatile cryptocurrency market and serve as a medium of exchange and store of value in DeFi.
Yield Farming
Yield farming involves earning rewards, usually in the form of additional tokens, by providing liquidity to DeFi platforms. Users can lend or lock up their assets in liquidity pools and earn yields based on the platform’s operations and demand.
Automated Market Makers (AMMs)
AMMs are a type of decentralized exchange that uses mathematical formulas to determine the price of assets based on the ratio of their supply. These algorithms enable continuous liquidity and trading, allowing users to swap tokens instantly.
Decentralized Insurance
Decentralized insurance protocols provide coverage against various risks in DeFi, including smart contract vulnerabilities, exchange hacks, and asset theft. Users can purchase insurance coverage using digital assets and receive compensation in case of loss or damage.
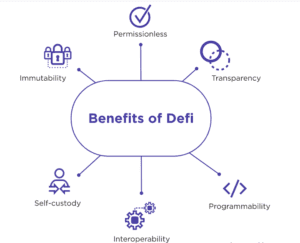
5. Benefits of DeFi
Financial Inclusion
DeFi opens up financial services to individuals who are unbanked or underbanked, providing access to savings, lending, and investment opportunities globally without relying on traditional banking infrastructure.
Enhanced Security
DeFi leverages blockchain’s cryptographic security features, making transactions secure, transparent, and resistant to tampering or fraud. Additionally, the use of smart contracts eliminates the need for intermediaries, reducing the risk of human error or malicious activities.
Greater Transparency
All transactions and operations within DeFi are recorded on the blockchain, allowing for transparent auditing and verification. This transparency builds trust among participants and reduces the risk of manipulation or fraud.
Interoperability
DeFi protocols are built to be interoperable, allowing different applications and platforms to seamlessly interact with each other. This interoperability fosters innovation, collaboration, and the development of a robust ecosystem of financial services.
Lower Costs and Efficiency
By removing intermediaries, DeFi eliminates the associated fees and delays. Transactions can be executed quickly and at a fraction of the cost compared to traditional financial systems, making financial services more accessible and affordable.
6. Challenges and Risks in DeFi
Smart Contract Vulnerabilities
Smart contracts are subject to coding errors or vulnerabilities, which can be exploited by malicious actors. Auditing and ensuring the security of smart contracts is crucial to mitigating these risks.
Regulatory Uncertainty
The regulatory landscape for DeFi is still evolving, with different jurisdictions applying varying regulations to cryptocurrencies and blockchain-based financial services. Uncertainty in regulations may pose challenges to DeFi’s growth and adoption.
Market Volatility
Cryptocurrency markets are known for their high volatility, which can impact the value of assets held within DeFi protocols. Sudden price fluctuations may result in liquidation events or loss of funds.
Liquidity Risks
DeFi platforms rely on sufficient liquidity to facilitate trading, lending, and borrowing. Insufficient liquidity can lead to higher transaction costs, slippage, and limited availability of services.
7. Future Outlook of DeFi
The future of DeFi holds immense potential for innovation and disruption in the financial industry. As the technology matures and regulatory frameworks evolve, we can expect increased adoption, scalability, and integration with traditional financial systems. DeFi has the potential to democratize finance, improve financial inclusivity, and redefine the way we interact with money and financial services.
8. Conclusion
Decentralized Finance (DeFi) represents a paradigm shift in the financial industry, leveraging blockchain technology, smart contracts, and decentralized applications to provide open, permissionless, and transparent financial services. DeFi offers numerous benefits, including financial inclusion, enhanced security, transparency, interoperability, and cost efficiency. However, challenges and risks, such as smart contract vulnerabilities and regulatory uncertainties, need to be addressed for the sustainable growth of DeFi. With ongoing developments and advancements, DeFi has the potential to revolutionize traditional finance and empower individuals globally.
9. FAQs
1. How can I participate in DeFi?
To participate in DeFi, you need a digital wallet, usually a cryptocurrency wallet, to store your assets. You can then interact with various DeFi protocols and DApps to lend, borrow, trade, or invest in different assets.
2. What are the risks associated with DeFi investments?
DeFi investments come with risks, including smart contract vulnerabilities, market volatility, liquidity risks, and regulatory uncertainties. It’s important to conduct thorough research, understand the risks involved, and only invest what you can afford to lose.
3. Is my investment in DeFi insured?
Most DeFi investments are not insured by traditional means, such as FDIC insurance for bank deposits. However, some DeFi platforms offer insurance coverage against specific risks. It’s essential to review the terms and conditions of each platform and understand the insurance coverage, if any, provided.
4. Can traditional financial institutions integrate with DeFi?
Yes, traditional financial institutions are exploring ways to integrate with DeFi. Some banks and financial institutions are partnering with DeFi projects or exploring the use of blockchain technology to streamline their processes and enhance efficiency.
5. What are some popular DeFi projects?
There are several popular DeFi projects, including Uniswap, Compound, Aave, MakerDAO, and Synthetix. These projects offer various financial services, such as decentralized exchanges, lending, borrowing, and synthetic assets.