Investment portfolio diversification is a strategy that involves spreading investments across different assets to reduce risk and potentially enhance returns. This article provides an overview of portfolio diversification, its benefits, key principles, different asset classes for diversification, implementation strategies, common mistakes to avoid, diversification in different investment strategies, and answers to common FAQs.
1. Introduction
Portfolio diversification is an essential concept in investment management that aims to reduce risk by spreading investments across various assets. Diversification helps investors mitigate the impact of individual asset performance on their overall portfolio and increase the likelihood of achieving long-term investment goals.
2. What is Portfolio Diversification?
Definition of Portfolio Diversification
Portfolio diversification is a risk management strategy that involves allocating investments across different asset classes, sectors, geographic regions, and investment styles. The goal is to reduce the potential impact of any single investment on the overall portfolio performance.
Importance of Diversification
Diversification is important because it helps investors minimize the impact of market volatility, reduce the risk of significant losses, and potentially enhance long-term returns. It allows investors to take advantage of different investment opportunities and balance the risk-reward tradeoff.
3. Benefits of Portfolio Diversification
Risk Reduction
Diversification helps reduce the risk associated with investing in individual assets. By spreading investments across different assets, investors can limit the impact of poor performance in one investment on the entire portfolio.
Enhanced Returns
Diversification can potentially enhance overall portfolio returns. By investing in different assets with varying return characteristics, investors have the opportunity to capture positive returns from different sources and balance out the performance of individual investments.
Protection Against Market Volatility
Diversification provides protection against market volatility. When one asset class or sector underperforms, other assets in the portfolio may offset the losses, reducing the overall impact on the portfolio’s value.
4. Key Principles of Portfolio Diversification
Asset Allocation
Asset allocation is the process of determining the ideal mix of different asset classes, such as stocks, bonds, real estate, and commodities, based on an investor’s risk tolerance and investment goals. It forms the foundation of a diversified portfolio.
Geographic Diversification
Geographic diversification involves investing in different regions or countries to reduce exposure to country-specific risks and take advantage of global economic opportunities. It helps mitigate the impact of regional economic downturns on the portfolio.
Sector Diversification
Sector diversification entails investing in different industry sectors, such as technology, healthcare, finance, and consumer goods. It allows investors to balance the performance of sectors that may have different market cycles and respond differently to economic conditions.
Time Diversification
Time diversification refers to spreading investments over different time horizons. By investing regularly over time, investors can reduce the impact of short-term market fluctuations and potentially benefit from the long-term growth of the markets.
5. Different Asset Classes for Diversification
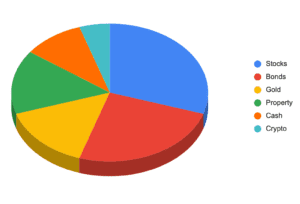
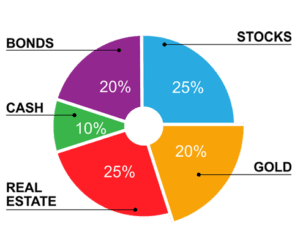
Stocks
Stocks represent ownership shares in a company and offer the potential for long-term capital appreciation. They can be further diversified by investing in different industries, market caps, and regions.
Bonds
Bonds are debt instruments issued by governments, municipalities, and corporations. They provide income through periodic interest payments and can help diversify a portfolio by adding stability and potential fixed income returns.
Real Estate
Real estate investments include properties such as residential, commercial, and industrial real estate. Investing in real estate can provide diversification benefits and potential income through rental yields and property value appreciation.
Commodities
Commodities include physical assets such as gold, silver, oil, natural gas, and agricultural products. Investing in commodities can provide diversification benefits as they often have low correlation with traditional asset classes.
Alternative Investments
Alternative investments, such as hedge funds, private equity, and venture capital, offer diversification beyond traditional asset classes. These investments can have different risk-return profiles and provide access to unique investment opportunities.
6. Implementing a Diversified Portfolio Strategy
Setting Investment Goals
Before implementing a diversified portfolio strategy, it is essential to define clear investment goals, such as capital appreciation, income generation, or wealth preservation. This helps guide the selection of suitable investments.
Assessing Risk Tolerance
Understanding risk tolerance is crucial in determining the appropriate level of diversification for an investor. Risk tolerance depends on factors such as age, financial goals, time horizon, and comfort with volatility.
Selecting Suitable Investments
Based on investment goals and risk tolerance, investors can select suitable investments across different asset classes and sectors. Careful consideration should be given to the risk-return characteristics of each investment.
Monitoring and Rebalancing
A diversified portfolio requires regular monitoring and rebalancing. As investments perform differently over time, the portfolio’s asset allocation may deviate from the target. Rebalancing involves selling overperforming assets and buying underperforming ones to maintain the desired asset allocation.
7. Common Mistakes to Avoid
Overconcentration
Overconcentration occurs when a portfolio is heavily weighted in a few investments or asset classes, increasing the risk of significant losses if those investments perform poorly. Diversification helps mitigate this risk.
Lack of Regular Monitoring
Failing to regularly monitor the portfolio’s performance and make necessary adjustments can lead to an imbalance in the asset allocation. Regular monitoring ensures the portfolio remains aligned with the investor’s goals and risk tolerance.
Emotional Decision-making
Allowing emotions to drive investment decisions, such as panic selling during market downturns or chasing the latest investment fads, can lead to poor investment outcomes. A diversified portfolio helps reduce emotional decision-making by providing a balanced approach.
8. Diversification in Different Investment Strategies
Passive Investing
Passive investing involves tracking a market index, such as the S&P 500, through index funds or exchange-traded funds (ETFs). Diversification is inherent in these strategies as they aim to replicate the performance of a broad market index.
Active Investing
Active investing involves actively selecting and managing individual investments to outperform the market. Even in active strategies, diversification plays a crucial role in managing risk and maximizing potential returns.
Index Funds and ETFs
Index funds and ETFs offer diversification by investing in a portfolio of securities that mimic a specific index. They provide broad exposure to different asset classes and sectors, making them suitable for diversification purposes.
Mutual Funds
Mutual funds pool money from multiple investors to invest in a diversified portfolio of securities. They offer diversification benefits across various asset classes and sectors, managed by professional fund managers.
9. Conclusion
Diversification is a fundamental principle of successful investing. By spreading investments across different assets, sectors, geographic regions, and investment styles, investors can reduce risk, enhance returns, and protect against market volatility. Implementing a diversified portfolio strategy involves setting investment goals, assessing risk tolerance, selecting suitable investments, and regularly monitoring and rebalancing the portfolio.
10. FAQs
1. How many investments should I have in my diversified portfolio? The number of investments in a diversified portfolio depends on factors such as the investor’s risk tolerance, investment goals, and available capital. However, having a minimum of 10-15 investments across different asset classes is often considered a good starting point.
2. Can I diversify within a single asset class? Yes, it is possible to diversify within a single asset class. For example, in the stock market, investors can diversify by investing in companies from different industries or of different sizes (large-cap, mid-cap, small-cap).
3. Is diversification a guarantee against losses? Diversification helps reduce the impact of losses from individual investments, but it does not eliminate the possibility of losses in the overall portfolio. All investments carry some level of risk, and diversification is a risk management strategy.
4. How often should I rebalance my portfolio? The frequency of portfolio rebalancing depends on various factors, including market conditions, changes in asset prices, and the investor’s long-term strategy. As a general guideline, portfolios are often rebalanced annually or when the asset allocation deviates significantly from the target.
5. Should I diversify my portfolio if I have a high-risk tolerance? Even if you have a high-risk tolerance, diversification is still important. It allows you to spread risk across different investments and reduce the potential impact of poor performance in any single investment. Diversification does not mean avoiding risk but managing it effectively.




2 thoughts on “Investment Portfolio Diversification”